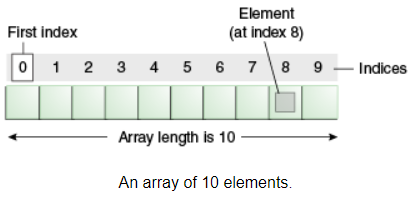
Array in java represents a group of fixed homogeneous elements that can be referenced with same variable. Array elements storage is index based and follow the mechanism of contiguous memory location which states that 1st element will store at index 0, 2nd element will store at index 1, 3rd element will store at index 2 and so on.
Arrays Class Hierarchy:
java.lang.Object java.util.Arrays
Arrays Class Syntax:
public class Arrays extends Object
Important points
- Array in java represents an object of a dynamically generated class.
- Arrays class extends Object class.
- Arrays in java represents object that’s why we can get length of an array using member length. In C/C++ sizeof operator is used to find the array length.
- Array in java can be used as a static variable, a instance variable or a method parameter/argument.
- Both primitive values or objects can be stored in Java array.
- Both single and multi-dimensional array can be created in java.
- The concept of anonymous array is also there in Java.
- Array represents the group of fixed elements. We cannot change the array size. Collection framework can be used as dynamic size group of items.
Arrays Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| get(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object. |
| getBoolean(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as a boolean. |
| getByte(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as a byte. |
| getChar(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as a char. |
| getDouble(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as a double. |
| getFloat(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as a float. |
| getInt(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as an int. |
| getLength(Object array) | It is used to get the length of the given array object, as an int. |
| getLong(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as a long. |
| getShort(Object array, int index) | It is used to get the value of the indexed component in the given array object, as a short. |
| newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int… dimensions) | It is used to create a new array with the given component type and dimensions. |
| newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int length) | It is used to create a new array with the given component type and length. |
| set(Object array, int index, Object value) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified new value. |
| setBoolean(Object array, int index, boolean z) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified boolean value. |
| setByte(Object array, int index, byte b) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified byte value. |
| setChar(Object array, int index, char c) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified char value. |
| setDouble(Object array, int index, double d) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified double value. |
| setFloat(Object array, int index, float f) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified float value. |
| setInt(Object array, int index, int i) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified int value. |
| setLong(Object array, int index, long l) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified long value. |
| setShort(Object array, int index, short s) | It is used to set the value of the indexed component of the given array object to the specified short value. |
Single Dimensional Array
Syntax: Declare an Array
dataType[] arr;
dataType []arr;
dataType arr[];
Syntax: Instantiate an Array
arrayReferenceVariable = new datatype[size];
Syntax: Insert elements to an Array
arrayReferenceVariable = {element1, element2, ..., elementn};
Example
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Creating array object String subjectArray1[] = new String[5]; //initializing subjectArray1[0]="Java"; subjectArray1[1]="Oracle"; subjectArray1[2]="SQL"; subjectArray1[3]="Spring"; subjectArray1[4]="Hibernate"; //Print array elements System.out.println("Elements of subjectArray1:"); for(int i=0;i<subjectArray1.length;i++) System.out.println(subjectArray1[i]); //Another approach to create an array //Creating array object String subjectArray2[] = {"Java", "Oracle", "SQL", "Spring", "Hibernate"}; //Print array elements System.out.println("Elements of subjectArray2:"); for(int i=0;i<subjectArray2.length;i++) System.out.println(subjectArray2[i]); } } |
Output
Elements of subjectArray1: Java Oracle SQL Spring Hibernate Elements of subjectArray2: Java Oracle SQL Spring Hibernate |
Change an Array Element
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Creating array object String subjectArray[] = {"Java", "Oracle", "SQL", "Spring"}; //Print array elements System.out.println("Array Elements:"); for(int i=0;i<subjectArray.length;i++) { System.out.println(subjectArray[i]); } subjectArray[2] = "Hibernate"; //Print array elements System.out.println("Array Elements after change:"); for(int i=0;i<subjectArray.length;i++) { System.out.println(subjectArray[i]); } } } |
Output
Array Elements: Java Oracle SQL Spring Array Elements after change: Java Oracle Hibernate Spring |
For-Each Loop on Java Array
Syntax: for-each
for (dataType variable : arrayName) {
...
}
Example
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Creating array object String subjectArray[] = {"Java", "Oracle", "SQL", "Spring"}; //Print array elements System.out.println("Array Elements:"); for (String subject : subjectArray) { System.out.println(subject); } } } |
Output
Array Elements: Java Oracle SQL Spring |
Passing Array as an Argument to a Method
public class Main { static void printArray(String[] subjectArray){ //Print array elements System.out.println("Array Elements:"); for (String subject : subjectArray) { System.out.println(subject); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //Creating array object String subjectArray[] = {"Java", "Oracle", "SQL", "Spring"}; //Passing array to method printArray(subjectArray); } } |
Output
Array Elements: Java Oracle SQL Spring |
Return Array from a Method
public class Main { static String[] createArray(){ //Creating array object String subjectArray[] = {"Java", "Oracle", "SQL", "Spring"}; return subjectArray; } public static void main(String[] args) { //Get array from a method String[] subjectArray = createArray(); //Print array elements System.out.println("Array Elements:"); for (String subject : subjectArray) { System.out.println(subject); } } } |
Output
Array Elements: Java Oracle SQL Spring |
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
JVM will throw ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if you want to access any array element from the negative index or from a index which is equal to or greater than array size. An array index can not be negative.
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Creating array object String subjectArray[] = {"Java", "Oracle", "SQL", "Spring"}; //Try to Print array element from 4th index System.out.println(subjectArray[4]); } } |
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 4 at Main.main(Main.java:8) |
Class Name of an Array
As we discussed earlier, Java arrays are the objects of dynamically created or proxy class. We can get the name of dynamically created class by reflection.
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create array int numberArray[]={11,12,13}; //retrieve class of array by reflection Class arrayClass = numberArray.getClass(); //Get class neme from class String arrayClassName = arrayClass.getName(); //Print array class name System.out.println("Array class name: " + arrayClassName); } } |
Output
Array class name: [I |
Multidimensional Array
Syntax: Declare an Array
dataType[][] arr;
dataType [][]arr;
dataType arr[][];
dataType []arr[];
Syntax: Instantiate an Array
arrayReferenceVariable = new datatype[rowSize][columnSize];
Syntax: Insert elements to an Array
arrayReferenceVariable = {{element11, element12, ..., element1n},
{element21, element22, ..., element2n}...{elementm1, elementm2, ..., elementmn};
Syntax: Insert elements to an Array
arrayReferenceVariable[0][0] = element11; arrayReferenceVariable[0][1] = element12; arrayReferenceVariable[0][2] = element13; arrayReferenceVariable[1][0] = element21; . . . arrayReferenceVariable[m-1][n-1] = elementmn;
Example
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Creating multi-dimensional array int numberArray[][]={{11,12,13},{21,22,23},{31,32,33}}; //Printing two dimensional array for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ for(int j=0;j<3;j++){ System.out.print(numberArray[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } } } |
Output
11 12 13 21 22 23 31 32 33 |
Cloning of an Array
We already discussed above that Array implements Cloneable interface and hence we can create clone of Array using clone() method.
Note: When clone method is applied to single dimensional array, it will do deep copy i.e. actual values but in case of multi-dimensional aaray it will create shallow copy i.e. references.
Example
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create array object String subjectArray[] = {"Java", "Oracle", "SQL", "Spring"}; //Print array elements System.out.println("Array Elements:"); for (String subject : subjectArray) { System.out.println(subject); } //Clone Array String clonedSubjectArray[] = subjectArray.clone(); //Print cloned array elements System.out.println("Cloned Array Elements:"); for (String subject : clonedSubjectArray) { System.out.println(subject); } } } |
Output
Array Elements: Java Oracle SQL Spring Cloned Array Elements: Java Oracle SQL Spring |
Addition of 2 Matrices
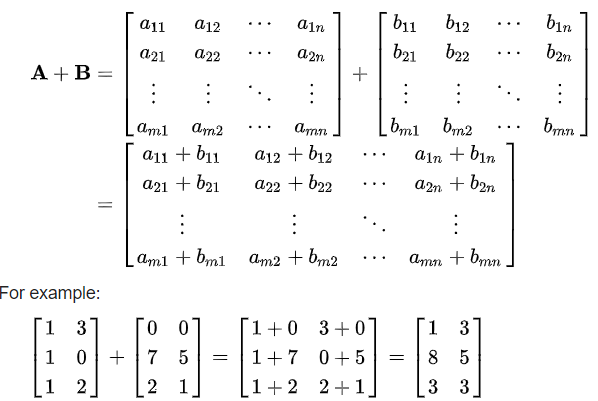
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create 2 matrices of 3x2 int a[][]={{1,3},{1,0},{1,2}}; int b[][]={{0,0},{7,5},{2,1}}; //Result matrix int c[][]=new int[3][2]; //add and print addition of 2 matrices for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ for(int j=0;j<2;j++){ c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j]; System.out.print(c[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } } } |
Output
1 3 8 5 3 3 |
Multiplication of 2 Matrices
Primary condition of multiplying 2 matrices is that columns of 1st matrix must be equal to rows of 2nd matrix.
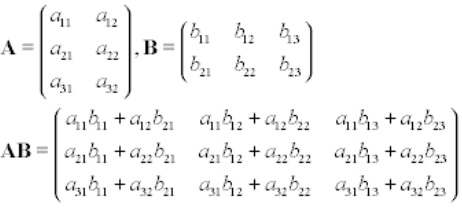
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create 2 matrices of 3x2 int a[][]={{1,3},{1,5},{1,2}}; int b[][]={{2,3,5},{2,1,6}}; //Result matrix int c[][]=new int[3][2]; //Print Multiplication of 2 matrices for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ for(int j=0;j<2;j++){ c[i][j]=0; for(int k=0;k<2;k++) { c[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j]; } System.out.print(c[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } } } |
Output
8 6 12 8 6 5 |
Anonymous Array
8 6 12 8 6 5 |
Output
8 6 12 8 6 5 |
Interview Questions on Arrays
- Can we change array size in java?
- What is an anonymous array in java?
- Difference between array and arraylist in java?
- What are jagged arrays in java?
- Can array size be negative in java?
- Java program to find duplicate elements in an array.
- Java program to find second largest element in an array of integers.
- Java program to check the equality of two arrays.
- Find all pairs of elements in an integer array whose sum is equal to a given number.
- Java program to find continuous sub array whose sum is equal to a given number
- Java program to find the intersection of two arrays
- Java program to separate zeros from non-zeros in an integer array
- Java program to find all the leaders in an integer array
- Java program to find a missing number in an integer array
- Java program to convert an array to ArrayList and an ArrayList to array
- Java program to count occurrences of each element in an array
- Java program to reverse an array without using an additional array
- Java program to remove duplicate elements from an array
- Java program to find union and intersection of multiple arrays
- Java program to find the most frequent element in an array
