Definition of derivative, relate it to the slope of the tangent of a curve, derivative of the sum, difference, product and quotient of functions
Differentiation relates to the measurement of change. For a linear function such as y = mx + b where b is the y-intercept and m is the constant slope. Here m is defined as:
![]()
The tangent line to the graph of y = f(x) at x = c is the line through the point (c, f(c)) with slope
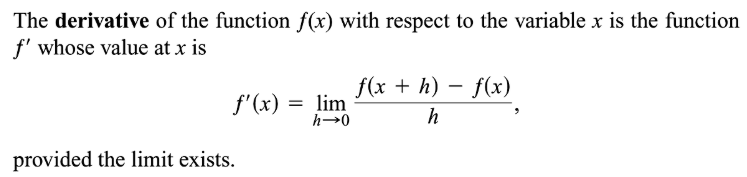
provided this limit exists. If the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) with respect to x exists at a point c, then it is the slope of the tangent line at that point.The derivative is the slope of the tangent line to a graph f(x) and is usually denoted f’(x).It is calculated by deducing the limit of the difference quotient as ∆x approaches 0. The process of finding the rate at which one variable changes with respect to another is called differentiation.
Derivative Function:
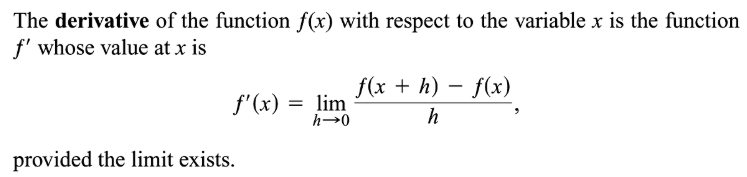
| Notation | Meaning |
| f’(x) | f prime of x |
| y’ | y prime |
| A noun, derivative with respect to x | |
| A verb, it means to take the derivative with respect to x |
Basic differentiation rules:
Constant rule
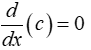
Here, c is a constant and the derivative of a constant function is zero.
Ex. f(x) = 5; f’(x)=0
Exponent rule
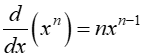
n is a real number. To find the derivative of f (x) = xn.Pull a copy of the exponent out in front of the term and subtract one from the exponent.
Ex. f(x) = x7, f’(x) = 7x6
Constant multiple rule
![]()
c is a constant and the derivative of a constant times a function is equal to the constant times the derivative of the function.
Ex. f(x) = 3x8 , f’(x) = 3(8x7)=24x7
Sum/difference rule
![]()
The derivative of a sum of functions is the sum of the derivatives and the derivative of a difference of functions is the difference of the derivatives.
Ex. f(x) = 7 + x12 ; f’(x) = 0 +12x11 =12x11
Product rule
![]()
Ex. f(x) = (x3 + 2x + 5 ) (3x7 -8x2 +1)
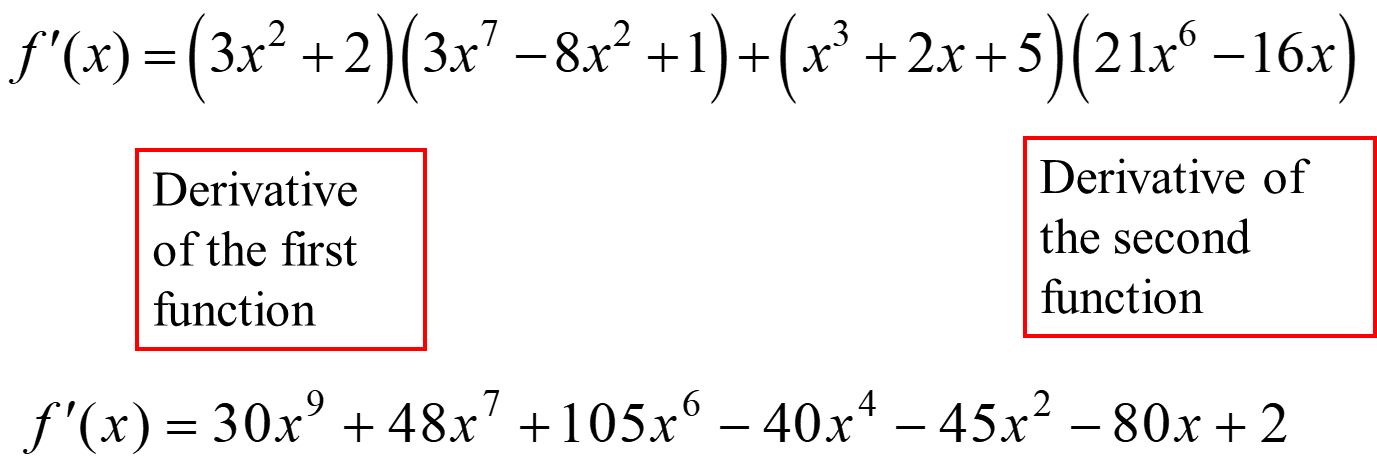
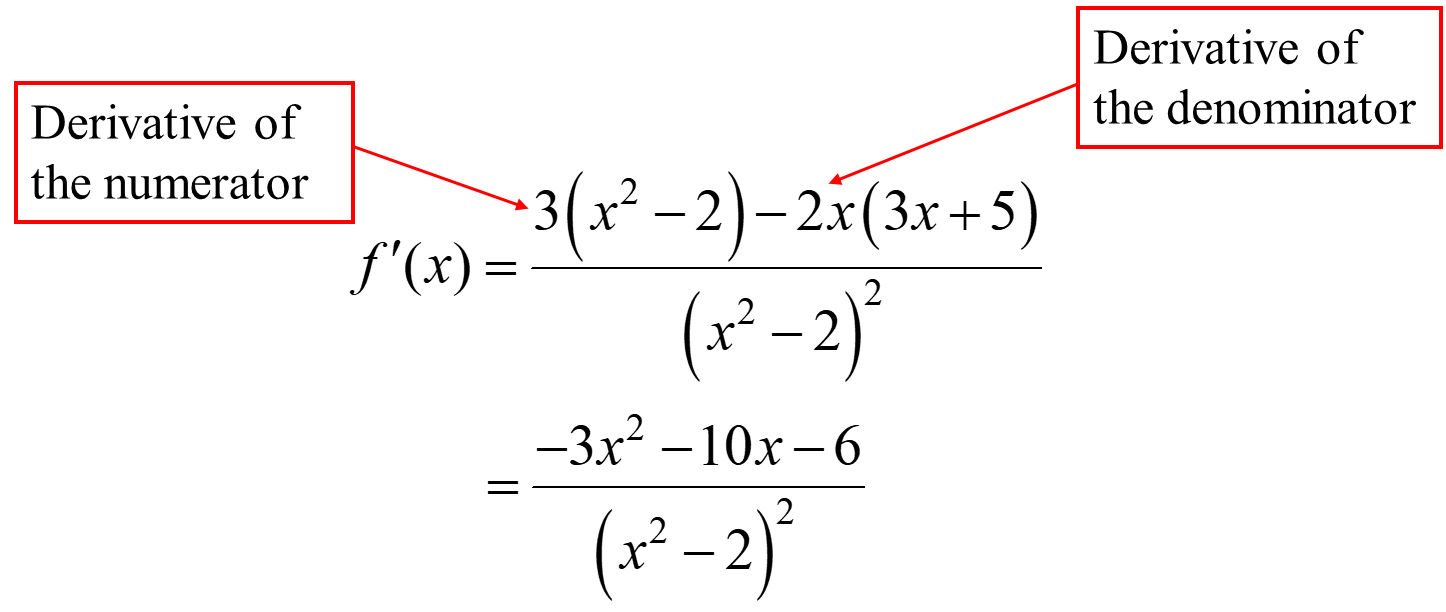
Quotient Rule
Ex.
The chain rule
If h(x) = g(f(x)) then h’(x) = g’(f(x))∙ f’(x). Note that here h(x) is a composite function. In other words, if y = h(x) = g(u), where u = f(x), then
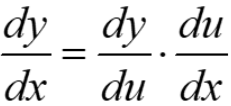
The chain rule develops the general power rule.
If h(x) = [f(x)]n where n is real then,
![]()
Ex.
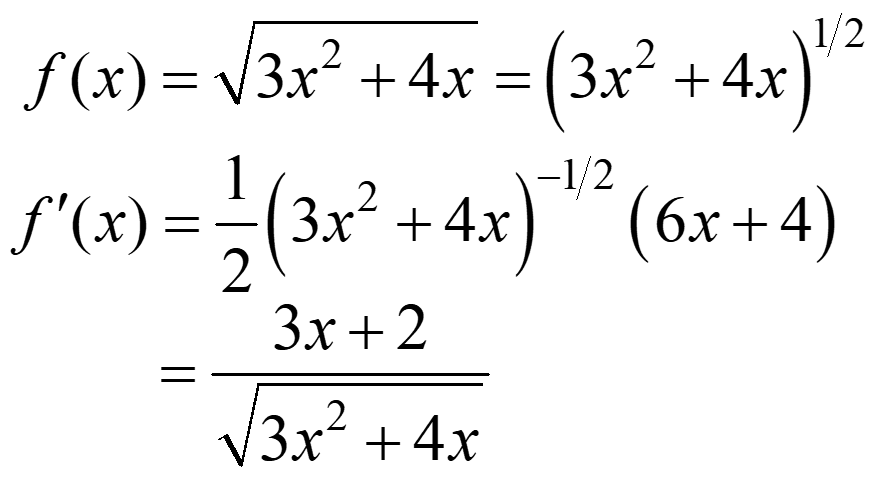
Ex.

