Exceptional handling:
Exception handling is a mechanism to handle runtime errors, so that normal flow of the program can be maintained.
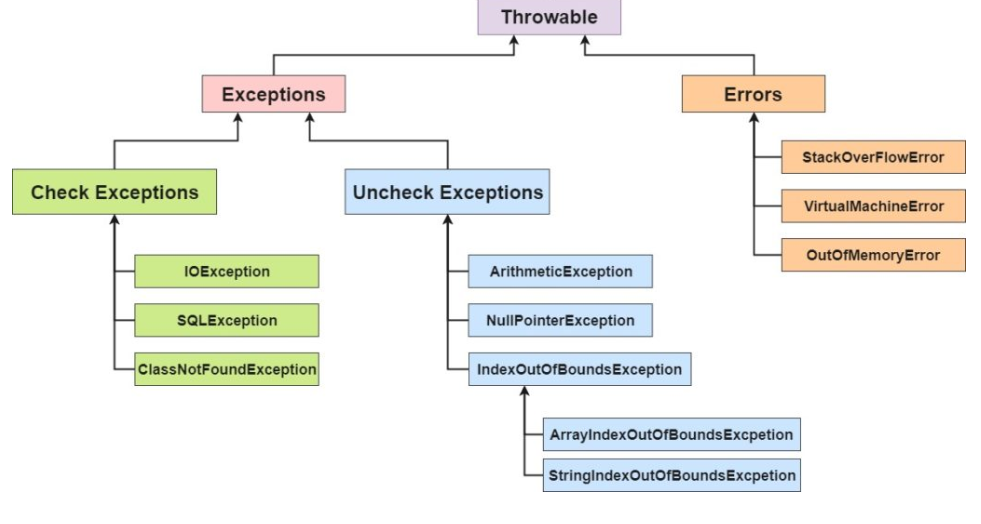
Exception Hierarchy:
Throwable is the super class.
Advantages/Benefits of exceptional handling:
- Using exceptional handling we can separate the error handling code from normal code.
- Using exceptional handling we can differentiate the error types.
- Normal flow of program can be maintained.
Types of Exception:
- Checked exception.
- Unchecked exception.
- Error.
Checked exceptions:
Checked exceptions are those exceptional conditions that are checked by compiler at the compile time. A checked exception forces you to either use try-catch or throws. All exceptions except Error, RuntimeException, and their subclasses are checked exceptions.
e.g. – IOException, SQLException etc.
Unchecked exceptions:
Unchecked exceptions are those exceptional conditions that are not checked by compiler at the compile time. Unchecked exceptions are checked at runtime. An unchecked exception not forces you to either use try-catch or throws. RuntimeException and their subclasses are unchecked exceptions. This Exception can be avoided by programmer.
e.g. – NullPointerException, ArithmeticException etc.
Error:
Errors are those exceptional conditions that are not checked by compiler at the compile time. Errors are checked at runtime. An error not forces you to either use try-catch or throws. Error and their subclasses are represents errors. Error can’t be avoided by programmer, it is irrecoverable.
e.g. – OutOfMemoryError etc.
How to write an exception handler?
To write a simple exception handler, first enclose the code that might throw an exception within try block. When an exception occurs in try block, it will be handled by an appropriate exception handler. Exception handler can associate with try block by using catch block or finally block after it.
Note: catch and finally block both can be attached with single try block. Hierarchy should be try-catch-finally.
To understand more, let us see the keywords used in exception handling.
- try
- catch
- finally
- throw
- throws
Next Topic: try and catch blocks in java with example.
Previous Topic: Some important terms for Exception Handling.
