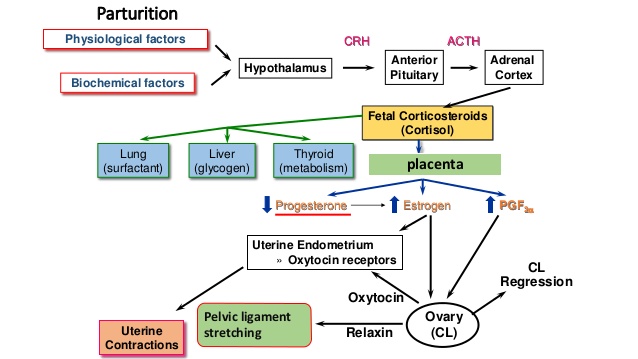
Parturition means childbirth. Childbirth is the culmination of pregnancy, during which a baby grows inside a woman’s uterus. Childbirth is also called labor. Pregnant women go into labor mostly after nine months of conception.
Dilation
The first stage of parturition begins when the labor starts. It continues until the cervix is fully dilated. This dilation is divided into two phases:
Latent phase. The cervix is 0 to 4 centimeters (cm) dilated.
Active phase. The cervix is 4 to 10 cm dilated.
It takes around six hours for a woman who’s giving birth for the first time in latent phase and takes about five hours for a woman who’s given birth before. For some women in case of complexity, the latent phase might last 8 to 12 hours.
In course of the active phase, for a woman who’s giving birth for the first time it’s presumed that the cervix will dilate at a rate of 1 cm per hour on the other hand a woman who’s previously had given birth, the rate is round about 2 cm per hour.
Expulsion
The second stage of parturition begin at complete dilation and proceeds on until the baby is delivered. This stage also has two phases:
Passive phase. The baby’s head moves down through the vagina.
Active phase. The mother have an urge to push, or shrink the abdominal muscles in time with the contractions.
The active phase continues about 45 minutes for a woman who’s delivering for the first time, where for the women who’ve had given birth before, the active phase continues for about 30 minutes. Stage 2 ends with the birth of the baby. At this time, the umbilical cord is attached, and breastfeeding is mostly suggested to help with stage 3.
Placental
Third stage of parturition comes after birth is given and ends with the delivery of the placenta and membranes. If the doctor is good in acting his role — with pulling on the placenta gently— this stage takes about five minutes. If the placenta is delivered without any help from the nurses or on its own, stage 3 can be around 30 minutes.
Complications during childbirth:
Fetal distress
Fetal distress typically refers to a slowdown in the baby’s heart rate. A doctor will usually handle this by using a vacuum extractor or forceps to quicken the birth. If that’s unsuccessful, a cesarean delivery might be called for. This is a surgery to deliver the baby.
Nuchal cord
This is when the umbilical cord wraps around the baby’s neck. Although a nuchal cord doesn’t mean danger for the baby, it could become a problem if the mother can’t push the baby out and a vacuum extractor or forceps are unsuccessful. Then a cesarean is necessary.
Breech
Human babies should be delivered with their head down. Sometimes a doctor can reposition the baby manually. Sometimes the solution is a cesarean delivery.
Thus, every woman experience is different.
